1. 思路
一种带边界盒的快速求交方案。
它假设平行的平面形成长方体,其中每一组平行于一个轴。
这种方法与Haines(1989)讨论的边界框计算非常相似,只是它减少了浮点运算的数量,并返回与长方体的交点,这在某些情况下是必需的,例如在体素遍历中,以识别光线穿透的第一个体素。
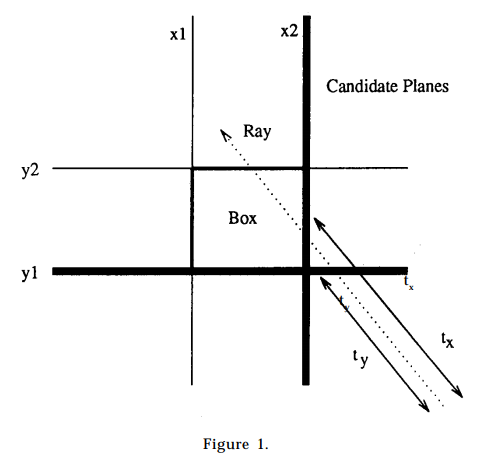
假设我们在三维环境中工作,我们首先搜索光线 可能相交的三个候选平面 ,也就是说,我们剔除形成长方体的后向平面。
从这三个候选平面来看,与候选平面的最大命中距离必须是光线击中的最近的平面(条件是命中在长方体内部;否则没有命中)。
例如,在 2D 中,设 x1 、 x2 、 y1 、 y2 为框的边界。
- 在本例中,光线的原点位于右下角,候选平面为 x2 和 y1 ;
- 然后分别计算从射线原点到 x2 和 y1 的 tx 和 ty 命中距离;
- 因为tx>ty , x2 是被射线击中的最近的平面。
1.2 步骤
- 射线公式:
p=porg+td
- 求各个分量的系数 t :
⎩⎪⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎪⎧tx=dxpmin.x−porg.x tx=dxpmax.x−porg.x
- porg 在 pmin 的左边
- porg 在 pmax 的右边
其余分量同理。
- 若射线的长度足够,足以与对应平面相交,此时便可直接求交点:
- tx=max{ tx, ty, tz} :射线可能与 yz 平面相交,先求射线在 x=xmin 或 x=xmax 面上的交点,再检测该交点是否在 AABB 对应的矩形面上;
- ty=max{ tx, ty, tz} :射线可能与 xz 平面相交,先求射线在 y=ymin 或 y=ymax 面上的交点,再检测该交点是否在 AABB 对应的矩形面上;
- tz=max{ tx, ty, tz} :射线可能与 xy 平面相交,先求射线在 z=zmin 或 z=zmax 面上的交点,再检测该交点是否在 AABB 对应的矩形面上。
2. 示例代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
|
float AABB3::rayIntersect(
const Vector3& rayOrg,
const Vector3& rayDelta,
Vector3* returnNormal
) const {
const float kNoIntersection = 1e30f;
bool inside = true;
float xt = 0;
float xn = 0;
if (rayOrg.x < min.x) {
xt = min.x - rayOrg.x;
if (xt > rayDelta.x) return kNoIntersection;
xt /= rayDelta.x;
inside = false;
xn = -1.0f;
}
else if (rayOrg.x > max.x) {
xt = max.x - rayOrg.x;
if (xt < rayDelta.x) return kNoIntersection;
xt /= rayDelta.x;
inside = false;
xn = 1.0f;
}
else {
xt = -1.0f;
}
float yt = 0;
float yn = 0;
if (rayOrg.y < min.y) {
yt = min.y - rayOrg.y;
if (yt > rayDelta.y) return kNoIntersection;
yt /= rayDelta.y;
inside = false;
yn = -1.0f;
}
else if (rayOrg.y > max.y) {
yt = max.y - rayOrg.y;
if (yt < rayDelta.y) return kNoIntersection;
yt /= rayDelta.y;
inside = false;
yn = 1.0f;
}
else {
yt = -1.0f;
}
float zt = 0;
float zn = 0;
if (rayOrg.z < min.z) {
zt = min.z - rayOrg.z;
if (zt > rayDelta.z) return kNoIntersection;
zt /= rayDelta.z;
inside = false;
zn = -1.0f;
}
else if (rayOrg.z > max.z) {
zt = max.z - rayOrg.z;
if (zt < rayDelta.z) return kNoIntersection;
zt /= rayDelta.z;
inside = false;
zn = 1.0f;
}
else {
zt = -1.0f;
}
if (inside) {
if (returnNormal != NULL) {
*returnNormal = -rayDelta;
returnNormal->normalize();
}
return 0.0f;
}
int which = 0;
float t = xt;
if (yt > t) {
which = 1;
t = yt;
}
if (zt > t) {
which = 2;
t = zt;
}
switch (which) {
case 0:
{
float y = rayOrg.y + rayDelta.y * t;
if (y < min.y || y > max.y) return kNoIntersection;
float z = rayOrg.z + rayDelta.z * t;
if (z < min.z || z > max.z) return kNoIntersection;
if (returnNormal != NULL) {
returnNormal->x = xn;
returnNormal->y = 0.0f;
returnNormal->z = 0.0f;
}
} break;
case 1:
{
float x = rayOrg.x + rayDelta.x * t;
if (x < min.x || x > max.x) return kNoIntersection;
float z = rayOrg.z + rayDelta.z * t;
if (z < min.z || z > max.z) return kNoIntersection;
if (returnNormal != NULL) {
returnNormal->x = 0.0f;
returnNormal->y = yn;
returnNormal->z = 0.0f;
}
} break;
case 2:
{
float x = rayOrg.x + rayDelta.x * t;
if (x < min.x || x > max.x) return kNoIntersection;
float y = rayOrg.y + rayDelta.y * t;
if (y < min.y || y > max.y) return kNoIntersection;
if (returnNormal != NULL) {
returnNormal->x = 0.0f;
returnNormal->y = 0.0f;
returnNormal->z = zn;
}
} break;
}
return t;
}
|
参考资料
参考书籍:《Graphics Gems I》 P395
